Infrastructure Facilities
Facilities Available
DEBEL has developed the requisite, modern design, assembly, integration, and test & evaluation infrastructure to offer reliable equipment and systems to the Armed Forces. These wide range of test facilities and indigenously developed rigs are extensively used during the design, development and testing phases, both by DEBEL and other agencies.

The High g environment of the current generation Aerospace Vehicles necessitate the Life Support Technologies to be tested to similar stresses in a controlled & simulated environment before being tested in the actual aerial vehicles. This necessitates the requirement of a high performance Dynamic Test Centrifuge on which the Life Support Systems could be mounted and tested in functional condition.
The High Performance Dynamic test centrifuge has been manufactured on DEBEL specifications. It has provisions to test the life support systems in operating condition and monitor the data on-line, Max Capability 20 g peak at an onset rate of 10 g/sec max, fully computerised, Max Payload 25 Kg, mounting options of payload in '+' or '-' x, y or z axes. It has Pneumatic supply provided through rotary joint and DC power through slip rings and on-line wire-less monitoring of 15 channel data along with g-signature. All possible safety measures are incorporated in the specification.

It enables the assessment of functioning of Submarine Escape Set with the help of instrumented dummy system in a vessel filled and pressurized with water for depths up to 200 m.
Breathing sequence using the gas mixture in the set is simulated in the chamber and gases released at different depths from the breathing apparatus by the submariners are analyzed in the TRIMIX gas analyzer. Provision of ascertaining the ascending rate of submariner is also provided in this test facility.

Aviation environment exposes the aviators to extremely high altitudes. With the Indian Human Space Program a reality, an environment akin to actual vacuum has become a reality. Hence, the Life Support Technologies being developed needs to be tested in a high altitude chamber having appropriate capabilities.
The man-rated High Altitude Chamber has been manufactured to DEBEL Specifications and is being built to PVHO standards. It has been so designed that any of the Life Support Equipment can be tested in functional condition with on-line monitoring of data.
It has the seating capacity of 4 persons in main and 2 in auxiliary chambers. Max altitude of main & Auxilliary chambers are 50000 ft and 100000 ft AMSL respectively, both having operations independent of each other. There is pneumatic compressed air & oxygen supply to each chamber. It has a provision of Rapid Decompression (RD) from 8000 ft to 23000 ft or 21000 ft to 50000 ft AMSL in 2 sec. There is also a provision to configure the RD from any altitude within a given pressure differential of about 5.5 psi. The functional data is obtained on-line for continuous monitoring.

CATH chamber can simulate pressure, temperature and humidity in its test space. It is also known as combined altitude, temperature and humidity chamber which is primarily used in R&D and testing of aerospace components including life support devices. The chamber meets many international standards including MIL and RTCA. The chamber capacity is 1000 Litre and is fully automatic with safety interlocks.
The CATH chamber has been manufactured to DEBEL specifications. The chamber can simulate altitude range from sea level to 10 mbar which is equivalent to 01 lakh feet ASL. The temperature range is from -70C to +180C and ramp rates starting from 5�C/min. The humidity range is 10% to 98% RH. Complex test standard such as CATH of MIL-STD-810G or RTCA DO-180 for airborne equipment are programmable using the envicom Graphite. The envicom Graphite is a colour touch screen using Siemens SIMATIC controllers.
The chamber has mono block construction with epoxy based electrostatic powder coated surface. The test space is made of pre-polished stainless steel ensuring vapour tight enclosure with no conduction between test space & exterior. Inside the test space the specimen is conditioned with laminar air flow for uniform airflow across the work space & test specimen. It can simulate the Temperature, Altitude and humidity profiles separately and in combination. The facility can be used for testing aerospace components including life support devices for fighter aircrafts. It can also be used for testing the ground equipment for Army, Navy and Air force.

The pneumatic shock testing machine is used for qualifying products for fighter aircraft application including the arrestor landing shock qualification for naval aircrafts for proving their capabilities of withstanding and performing under severe mechanical shocks.
The Pneumatic Shock testing machine can simulate accelerations from 15 to 200 "g" with a load capacity of maximum 250kgs. The machine has been manufactured to MIL specifications and can simulate waveform like Half Sine, Saw tooth, Square and Trapezoidal pulses with minimum pulse width of 3 milli seconds to maximum pulse width of 40 milli seconds at the rate of 1 to 8 shocks per minute. The pneumatic shock test machine produces a shock pulse in the vertical direction using compressed air to force the carriage to generate impact on the shock machine base that are controlled, reproducible and accurate. Rubber pads are used between the platform and the base in the impact area to produce shock pulses. The basic structure of the machine is heavy steel which will not deteriorate under repeated shocks. The platform is supported and guided by the lifting and driving piston rod. Friction brakes are used as a rebound brake and as a quick release device. A microprocessor control is available to provide a single point for shock machine set up. A PC based Shock controller & waveform monitoring system with Window based application software is provided to monitor acceleration level, waveform duration, shock count etc. on 19" colour monitor with facility of zoom. The controls for the machine are mounted in a control panel on the front of the machine. The structure is supported on four passive air springs with dampers to isolate the shock from the floor. The facility can be used for testing aerospace components including life support devices for fighter aircrafts. It can also be used for testing the ground equipment for Army, Navy and Air force.

This test facility is designed for functional evaluation and qualification of On-Board Oxygen Generating System (OBOGS). It has capability to carryout the on-ground and simulated high altitude tests. It consists of vacuum chamber fitted with two high flow rotary vacuum pumps with necessary pneumatic and electronic controls. The functional tests under various simulated conditions carried out on this facility demonstrate that the system meets the entire design specification requirement in respect of function, operational performance and safety.

Pneumatic Test Rig
The pneumatic test rig is designed to carry out the performance evaluation of QDC for its acceptance and qualification. It has pressure and flow controllers with necessary instrumentation for various tests of QDC. It has capability to carryout leakage, flow and pressure drop tests.

Pullout Test Rig
The tester is designed to test the QDC for positive locking and unlocking force to detach the seat part from aircraft part of QDC which happens during the seat ejection. The QDC aircraft part is mounted in the bottom fixture provided on the rig and the lanyard cable of the seat part is fixed in the upper fixture hook which is fitted to the load cell. The load cell has peak hold facility to record the maximum load during the detachment of the QDC. The movable top beam of the tester is moved up and down by means of a motor whose speed is controlled though a potentiometer.

The functional tests of DOR are conducted in this test rig which is built around a high altitude chamber. The rig is especially suitable for simulating Rapid Decompression Scenarios and positive pressure generated in the DOR at various altitudes. The Unit under test is mounted in high altitude chamber and appropriate valve combinations are chosen to achieve the required pneumatic circuit combinations for carrying out the test as per the QTP document of DOR. Required pressures and flows are applied through the pressure regulators and flow control valves and various functionalities and the leak rates are recorded with the help of the flow meters, pressure gauges. The high altitude chamber simulates MAX of 60000 ft AMSL.

This pneumatic based rig has a provision to create various rates of inspirations with an option to set the tidal volume. It is extremely helpful in endurance testing of the breathing systems and assemblies.

The automatic breathing simulator is a device which is used for simulating human breathing. It consists of a stainless steel bellow driven by a servo pneumatic system under displacement control. It is intended to follow position demand waveforms which generate air flow / breathing profiles and is controlled from a computer program interfaced to a PC via an Ethernet link. The bellow assembly with a pneumatic actuator propel air / oxygen-enriched air mixtures between pressures of 2 to 1200mbar absolute. It is suitable for placing inside an altitude chamber with altitude upto 50,000 ft AMSL. Various breathing waveforms can be generated with a facility to control and monitor various relevant parameters like flow, tidal volume, breathes per minute, peak flow, rate of change of flow etc. The bellows assembly can be located inside an altitude chamber with the monitoring system located outside the chamber.

Anti-G Valve

Test Rigs
The small test centrifuge has been the backbone of the anti-G valve testing till now. It is a small yet computer controlled centrifuge meant for mounting small weight loads. It has a rotary pneumatic joint for compressed gas supply and on-line data acquisition. It essentially tests the anti-G valve dynamic performance.
This consists of a static test rig in which the acceleration loading on the anti-G valve is imposed in the form of multiple weights and the output pressure is read in the rig. It is also used to measure the leakage.

The test rig is designed and developed to carry out the pneumatic performance tests of high pressure oxygen system. The test rig is also fitted with an electronic module to indicate the various warnings wrt to oxygen content in the cylinder etc. generated using the electrical signal from the unit under test. All the flow meters on the test rig are mounted on the vertical panel and the control valves and pressure indicators are fixed on the horizontal panel. The unit under test shall be placed on the platform provided by the side of the test rig.

Personal Equipment

Connector (PEC) Test Rig
The functional tests on PEC are conducted on two separate test rigs. One is for the evaluation of unlocking force and the electrical continuity between the spring loaded connectors and the other for carrying out the leakage tests. The first one has a PEC test block with DOR-AGV interface for simulating the ejection seat separation. The unlocking force is measured by fitting PEC on the test block and pushing the plunger in the test block with the help of a load cell. The unlocking force can be directly read from the load cell read out. The continuity between the electrical connectors can be read from the display fitted on the test rig.
The second test rig is for measuring leakages which is built around a sealed leak chamber. The unit under test is placed inside the chamber after making the necessary pneumatic connections. Required pressure is applied through the pressure regulators and the leak rates are recorded with the help of the flow meters.

This test rig has been created to test the PPO2 oxygen sensor (OS) designed and developed by DEBEL. It creates a different oxygen concentration gas mixtures and varying OS heater temperatures to characterise the sensing by the OS. The test rig has become very useful in the on-going ILSS program of DEBEL.

This is a test rig for comprehensive testing of the ILSS. All the LRUs of the ILSS are mounted on a test platform, connected with the requisite pneumatic system with the output gas supplied to the oxygen mask and anti-G suit of the test dummy and tested accordingly. The breathing simulator is also connected. In this test rig, the normal functions as well as failure conditions are created and the system tested for full functional capabilities.

ECU Test Rig is used to simulate various inputs, monitor outputs and to verify the functional specifications of the ECU during normal laboratory tests as well as during ESS Tests. The Test Rig is realized using an Industrial PC with off the shelf available USB modules and an application specific hardware module. The various ECU I/Osare brought to a patch panel / terminal box through which signal monitoring / break in is possible.

Extreme Environment

Simulation Walk-in Chamber
A multi temperature programming capable Extreme Environmental Simulation Walk-in Chamber used for the evaluation of protective equipment used in Extreme Hot and extreme cold environment. The test facility has a temperature range of - 60 deg to + 70 deg C. The walk-in chamber is equipped with four observation windows and one IR transparent window for the evaluation of the prototypes developed. The chamber has about 20 Cum internal capacity and is safe for subjecting human subjects though it is conducted under supervision of a medical doctor.

CNC Vertical

Machine Centre
CNC vertical machining centre with an automatic tool changer and a rotary table is very useful for machining components out of Stainless Steel, Aluminium, Naval Brass. The machine fitted with automatic tool changer provides Least cycle time for tool change-over, which brings down overall cycle-time during multiple operations. The Agni++ series of VMC has optimum harmonic stability and maximum damping during demanding cutting conditions. This makes it possible to machine precision components.

Thermo Gravimetric Analyser (TGA) is an analytical instrument used for the determination of thermal degradation of textiles, rubbers, composites, plastic etc in controlled atmosphere. Change in the mass of the sample is studied while the sample is subjected to controlled temperature programmed ramp either linear or isothermal.
TGA is inherently quantitative; therefore, it is an extremely powerful thermal technique. TGA is mainly used for Thermal stability determination, Material characterization, Analysis of blends and Kinetic and corrosion studies.

Differential Scanning Calorimetry coupled with microscope (DSC-M) measures the temperatures and heat flows associated with the transitions of the materials as a function of time (or temperature) in a controlled atmosphere. The microscope coupled with the equipment provides online visual changes that take place during the transition of the material.
DSC-M can be used for- Glass transition temperature, Crystallization / Melting, Specific heat, Oxidative / thermal stability, Reaction Kinetics, Purity.

Micro encapsulation reactor is used for encapsulating Phase Change Material (PCM). The microcapsules in which PCM is encapsulated are coated onto the fabric that finds application in near body thermoregulation.
The reactor can be used for development of microcapsules coated fabrics having Phase Change materials, Mosquito repellents, CW/ BW decontamination agents.

Rotary evaporator is used in chemistry laboratories for the efficient and gentle removal of solvents from samples by evaporation under reduced pressure below their boiling point. The equipment is extremely useful in removing and separating thermally labile solutes dissolved in high boiling solvents much below the boiling point of the solvent.

Radio frequency (RF) sputtering, is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) method, for deposition of thin films. This involves ejecting material from a "target" which is a source, onto a "substrate" such as a silicon wafer, glass, etc.
Advantages are
- Multiple targets can be used for creating multilayer films & doping.
- Deposition of compound materials such as Oxides and Nitrides, through reactive sputtering.
Applications include
- Deposition of sensor material in the form of thin films.
- Deposition of metallic thin films for electrodes and other semiconductor devices.

An anechoic chamber is a room which simulates the free field acoustic i.e. a room without walls. Acoustic Anechoic chamber is designed to completely absorb reflections of sound waves and also provide isolation from exterior sources of noise. The combination of both aspects ensures that chamber simulates a quiet open-space of infinite dimension (free field condition) and avoids exterior noise source influences. Anechoic chambers nominally have sound energy absorption level of 99% to 100% or a reflected sound pressure level of 10% or less.
The performance evaluation of Electro-Acoustic Devices i.e. Microphones, Earphones and Bone Conductive devices is being carried out inside the Acoustic Anechoic Chamber as recommended in JSS and Military standards. These electro-acoustic devices are being used in Aircrew Helmet and Oxygen Mask for communication. The Anechoic chamber is also being used for noise attenuation performance of Aircrew Helmets and Ear defenders.

Advanced Electro-Acoustic Test Facility

Advanced Electro-Acoustic Test Facility
An advanced Electro - Acoustic test facility is intended for evaluating of microphones and earphones while being integrated in the Oxygen Masks and Helmets. The Electro - Acoustic Test Facility consists of state of art Bruel & Kjaer equipments such as Head and Torso Simulator, Generator module LAN-XI, Power Audio Amplifier and Pulse Electro-acoustic software modules. Head and Torso Simulator consist of a mouth simulator and two ear simulators. It provides the simulation of the acoustic field around a human head and torso. Performance parameter of Microphones and Earphones such as Output response, Frequency Response, Total Harmonic Distortion and Impedance curve can also be evaluated. The facility is also capable of evaluating Aircrew Helmets & Ear defenders for Noise Isolation characteristics and recording of environmental noise.

Universal Testing Machine is used to find the mechanical properties of materials in terms of properties such as tensile and compressive strengths behaviour including, textiles, polymers, rubbers composites, springs. This machine has the provision to carry out these testings only at Ambient conditions. Facility is also available to test the tensile strength of individual yarns and filaments. The tensile tests can be performed up to 100 kN while the existing accessories for compressive test permits strength determination only up to 20 kN. Machine can be operated either in stress controlled mode or strain controlled mode. The machine also has an extensiometer for accurate determination of sample deformation. The bursting strength of fabrics can also be determined with this machine.

Optical Distortion Testing Equipment is used to test the visors for optical distortions so that aircrew get clarity of images when they see through them. It consists of an illuminated coarse grating whose image is focused on affront coated mirror by the imaging optics. When there is no transparent object between the grating and the optics, undistorted grating image is focused on to the mirror. When a transparent object like visor is interposed between the grating and the optics, the grating image may get distorted due to the imperfections in the visor which is classified as acceptable and unacceptable based on the severity of the distortion. The acceptable and unacceptable distortion patterns shall be as per the figures shown in Para 4.4.5. of MIL- DTL - 43511D.

Ultraviolet and Visible spectrophotometers have over the period become the most important analytical instrument in the modern day laboratory for stability evaluation, stoichiometry determination and qualitative and quantitative determination of different analytes such as transition metal ions, highly conjugated organic compounds such as dyes, and biological molecules. UV-visible-NIR spectroscopy of textile fibres is one of the most common applications of the technique. In the visible-NIR range, detailed spectral information is recovered from the sample about the dyes and pigments used to color the fibre. Typical uses encompass quality assurance testing and product development measurements on textiles, dyes, pigments, papers and glass.

Pressurised liquid extraction (PLE) is a technique for extracting the compounds from solid and semisolid samples with liquid solvents. PLE system uses organic and aqueous liquid solvents at elevated temperatures and pressures to increase the efficiency of the extraction process. Increased temperature accelerates the extraction kinetics, and elevated pressure keeps the solvent liquid above its boiling point, ensuring safe, rapid extractions. Additionally, the pH-hardened pathway allows the extraction of matrices that are pretreated with acids or bases. Pressurised Liquid Extraction is not restricted to material analysis but is widely used in areas like Natural Products, Pharmaceuticals and Food Science. This method meet the requirements for extraction under US EPA SW-846 Method 3545A for Pressurized Fluid Extraction of base/neutrals and acids (BNA), organophosphorous pesticides (OPP), chlorinated pesticides and herbicides, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB), polychlorinated dibenzo-dioxins (PCDD) and polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDF), and diesel range organics (DRO). Pressurised liquid extraction technique replaces Soxhlet, sonication, wrist shaking, and other extraction techniques, and uses less solvent and less time.

Nanotechnology is one of the most important fields of research in the 21st century and DRDO has come up actively with its own program of research in this field. Nanotechnology make one capable of doing fabrication and measurements at nano-level precision leading to quantum leap in the properties of various systems in the selectivity, sensitivity and miniaturization of sensors and detectors. The nanotechnology enabled products have helped mankind to improve efficiency in various fields of life, may be by improving stamina and vigour and to make them capable of surviving and working effectively in adverse environment or by the timely detection of any adverse environmental or physiological threats. The nanomaterials of required size, shape and activity can be achieved only by the optimization of the synthesis process through systematic variation of different parameters affecting the process and characterization of the materials, especially the particle size and the Zeta Potential at every such step is very critical for this purpose.

Tescan Vega-3 LMU is a variable pressure SEM that supplements all the advantages of the high vacuum model with an extended facility for low-vacuum operations, enabling the investigation of conductive and nonconductive specimens in their natural, uncoated state. The 4-lens Wide Field optics design allows fully electronic control of beam aperture as well as a wide range of special imaging scanning modes. The system offers the wide magnification range (2.5 X to 1,000,000 X), from ultra-low magnification "macro" imaging to high resolution imaging and Structural, morphological, texture, fracture analyses and elemental analysis of metals, ceramics, polymers, composites, coated surfaces, biomaterials, etc.

Synergy H1 can be used for a wide range of applications in fluorescence, luminescence, UV-Vis and more for cell based assays, Biomarker Assays, Micro-volume analysis of nucleic acid and protein, Kinetic assays, ELISA, Genetic analysis, cell proliferation, cytotoxicity, drug absorption and metabolism, environmental monitoring etc. Detection modes: UV-Vis absorbance, Fluorescence intensity, Luminescence, Fluorescence polarization, Time-resolved fluorescence

The microscope can be used for identification of structures in fixed and live biological samples, Imaging, Material analysis, Optical microscopy etc.

Identification of functional group and structure elucidation, Identification of substances, Studying the progress of reaction, Detection of impurities, Quality control, Quantitative analysis of organic and inorganic molecules, polymers, plastics, etc.

Measurement of heavy metal contamination in air, water or soil samples; analysis of food for safety and nutritional content; to study drug efficacy and metabolism in drug research and development; to study degradation and contamination of various lubricants and oils. Applications include testing biofuels for batch consistency and quality control, as well as trace elemental analysis to ensure optimum performance, elemental profiling, quality control, nutritional labeling, determination of amount of contamination from mines, evaluation of specific elements in food, pharmaceuticals and petrochemicals, use in medicine for biological monitoring, use in pathology, use in evaluating nanomaterials.

Quantification of drugs, analysis of natural contamination, forensics, clinical testing, for analyzing complex mixtures, purifying chemical compounds, developing processes for synthesizing chemical compounds, isolating natural products and predicting physical properties of biomaterials. It helps in both qualitative and quantitative identification and/or estimation of the toxic chemicals as well as its degradation products. It is also used for finding out the degradation products and other contaminants of biomedical interest. It is used in quality control to ensure the purity of raw materials, to control and improve process yields, to quantify assays of final products, to evaluate product stability and monitor degradation. In addition, it will be used for analyzing air pollutants of the confined environment.

It works on the 'oxygen consumption' principle to evaluate the flammability behaviour of textiles and rubber specimens as per ASTM E 1354/ISO 5660. A total of 16 parameters that affect the burning behaviour of textiles/rubbers/polymers or any organic materials can be obtained.
The equipment is capable of measuring heat release rate, mass loss rate, time to ignition, effective heat of combustion etc. It consists of conical heater, temperature controller, ignition circuit, load cell, specimen holder, heat flux meter, calibration meter, exhaust system, smoke detection system, gas sampling and analysis system, digital data collection system and FTT ConeCalc software.

The tester predicts the amount of thermal protection a FR fabric or an assembly of fabrics would provide if exposed to a flash fire as per (ASTM D 4108-87). The time required to cause onset of second degree burns can be obtained from the above equipment. Equipment meets the NFPA 1976 and NFPA 1971 for Thermal Protective Performance. The measured heat is compared with the thermal tolerance of human tissue (Stoll & Chianta Curve) and time to 2nd degree burn injuries is predicted. The data acquisition package is capable of testing materials with accuracy, repeatability and convenience.

The AFT 45 Flame Chamber automatically measures the flame-spread time (rate of burning) of textile specimens burned at a 45� angle under controlled flame-impingement conditions as per ASTM D 1230.

The LIFT apparatus is intended to measure the rate of burning of Polymers, textiles, rubbers and plastics as per ISO 1320.

The smoke tester is intended for measuring the smoke density and other related parameters.

LOI is used for measuring the quantity of oxygen required to sustain the combustion of textiles and plastics as per ASTM 2863.

This facility is used for prediction and assessment of the injury levels due to shock wave produced by bomb blast.
It is meant to be used for developing human response model to mine blast & blast debris and evaluation of various anti mine protective gears.
It shall also be used for various applications where effect due to blast needs to be quantified and protection systems to be developed accordingly. DEBEL has the expertise for the simulation of various protective structures subjected to blast pressure wave and for testing the efficacy of the structure for better structural development.

This is a DEBEL designed test rig exclusively for the Submarine Escape Suit. The reducer head of the helium/heliox cylinders are tested for its performance by simultaneously connecting it with the breathing bag.

The Pressure breathing oxygen mask is an essential aircrew protective equipment which delivers the breathing gas to the aircrew made available by the breathing regulator of the aircraft. It becomes essential for the mask not to pose additional resistance to the breathing, or cause leakages. DEBEL has designed an automated Oxygen mask test rig that can test the mask for all its pneumatic functions. The test rig has various flow & pressure controllers with solenoid valves. It also has a digital sensor.
The test rig has two head forms to cater to different sizes of the oxygen mask. Once the mask is mounted on the head form, all tests can be completed within a short time. The test results are presented in a form that compares it against the laid down standards.
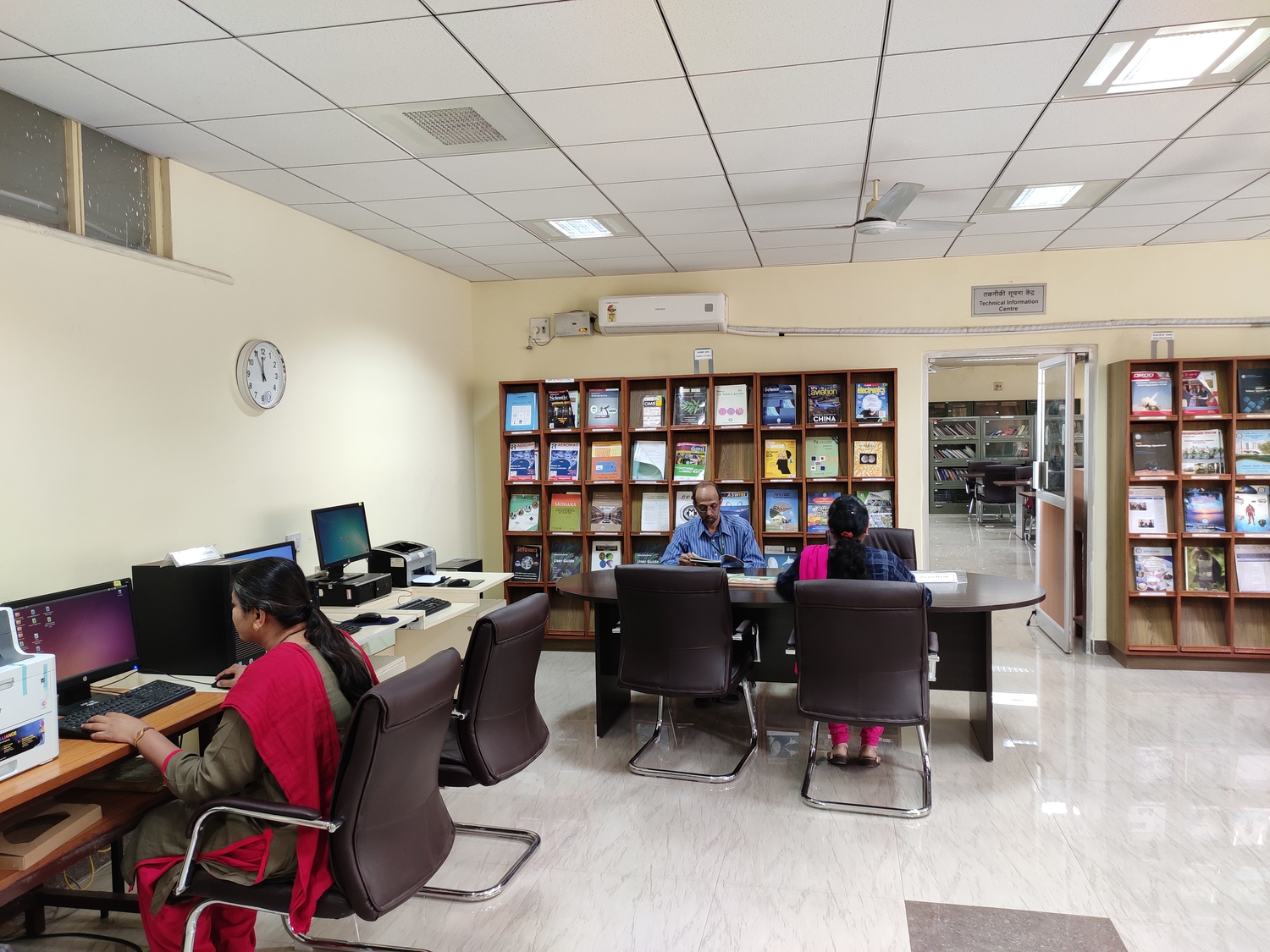

DEBEL is a multidisciplinary laboratory carrying out various project activities comprising different disciplines like Biomedical engineering, Biotechnology, Biosensors, Chemistry, Computer science, Electronics, Mechanical engineering, Material Sciences, Physics, Mechanical Engineering, Microbiology, Nanotechnology, Polymers, Textiles and so on. The Technical Information Centre (TIC), DEBEL caters to all the domain requirements of officers and staff in DEBEL, apart from the information needs for Society of Biomedical Technology (SBMT) projects for R&D activities related to medical devices technology.
TIC has a collection of 4800 books; 1017 standards; 304 reports, and 1895 bound volume of journals. Presently we are subscribing to 19 core print journals related to DEBEL’s R&D activities.
TIC provides various Information Communication Technology facilities like Intranet, Internet, DRONA, E-journal services, E-library services, DRDO e-journal consortia services etc. TIC is automated using ‘Koha’, an open source integrated library management software. ‘Koha’ is functional for circulation and Online Public Access Catalogue (OPAC) facility. We also have various other services like Inter Library Loan facility from DRDO and Non-DRDO TICs, reference, referral and reprographic services, Current Awareness Services (CAS), Selective Dissemination of Information (SDI) etc.